Soma pill is a muscle relaxant used for short-term relief of musculoskeletal pain. Its presence in the body varies based on factors like metabolism, dosage, and overall health, with typical detection windows ranging from 24 hours in blood to up to 90 days in hair.
Soma, also known by its generic name, Carisoprodol, is a muscle relaxant commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and discomfort caused by muscle injuries and spasms. While it can be effective in providing relief, understanding how long Soma stays in your system is crucial for safe and responsible use.
This comprehensive guide aims to explore the pharmacokinetics of Soma, the factors that influence its detection time, and the implications for users. Whether you are considering Soma for muscle pain relief or are currently using it, this information will help you make informed decisions about its usage and potential effects on your health.
What Is Soma?
Soma, or Carisoprodol, is a prescription medication classified as a muscle relaxant. It is primarily used to relieve discomfort associated with acute musculoskeletal conditions, such as muscle spasms or injuries. By acting on the central nervous system, Soma helps to relax muscles and alleviate pain, making it a valuable option for patients recovering from injuries or undergoing physical therapy.
Typically prescribed for short-term use, Soma is intended to be used in conjunction with rest, physical therapy, and other treatments to enhance overall recovery. While it can be effective in managing pain, it is essential to use Soma under the guidance of a healthcare professional due to its potential for misuse and dependence.
How Soma Works In The Body?
Soma pills function primarily as a muscle relaxant by influencing the central nervous system (CNS). It may alter the way the brain perceives pain signals. By inhibiting certain neurotransmitters in the brain, it can reduce the sensation of pain, leading to increased comfort for the individual.
By affecting the transmission of signals between the brain and the muscles, Soma promotes muscle relaxation. This can help relieve the stiffness and tension that often accompany musculoskeletal conditions.
Due to its effects on the CNS, Soma can cause sedation and relaxation, which may be beneficial for patients experiencing muscle pain. However, it is crucial to use this medication as prescribed and to be aware of the potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms with long-term use.
Factors Influencing Soma's Duration In The System
The duration that Soma pills stay in the body can vary significantly based on several individual and external factors. Understanding these factors can help users anticipate how long the medication may remain detectable and its potential effects.
Metabolism
Each person's metabolic rate plays a crucial role in how quickly medications are processed and eliminated from the body. Individuals with faster metabolisms may clear Soma more quickly, while those with slower metabolisms may retain the drug for a more extended period.
Age
Age can impact how the body metabolizes drugs. Older adults often experience slower metabolism and may have reduced liver and kidney function, leading to prolonged effects and detection times for Soma.
Dosage and Frequency of Use
The amount of Soma taken and how often it is used directly influence its duration in the system. Higher doses and frequent use can lead to accumulation in the body, extending the time it remains detectable.
Route of Administration
Soma is typically taken orally in tablet form. The route of administration can affect how quickly the drug enters the bloodstream and how long it stays active in the system.
Overall Health
Pre-existing health conditions, particularly those affecting the liver and kidneys, can significantly impact drug metabolism and clearance. Individuals with compromised liver or kidney function may experience longer durations of drug presence in their systems.
Other Medications
The use of other medications can interact with Soma and alter its metabolism. Certain drugs can either increase or decrease the rate at which Soma is processed, affecting how long it stays in the body.
Body Composition
Factors such as body weight, body fat percentage, and hydration levels can influence how drugs are stored and eliminated from the body. Individuals with higher body fat percentages may retain lipophilic drugs for longer periods.
Genetic Factors
Genetic variations can affect how individuals metabolize drugs. Some people may have genetic predispositions that influence their response to Soma and its duration in the system.
Detection Times For Soma
Understanding how long Soma pills can be detected in the body is essential for various reasons, including drug testing, medical supervision, and personal awareness of its effects. Detection times can vary based on the method of testing and individual factors. Here’s an overview of the typical detection times for Soma pills.
Blood Tests
Soma is generally detectable in the bloodstream for about 24 hours after the last dose. Blood tests are often used in medical settings or in situations where immediate results are needed, such as for monitoring compliance with prescribed treatments.
Urine Tests
Urine tests are the most common method for drug detection and can typically identify Soma for 1 to 7 days after ingestion, depending on several factors, including dosage, frequency of use, and individual metabolism. In some cases, particularly with heavy or prolonged use, Soma may be detectable for a more extended period.
Hair Tests
Hair follicle testing can provide a longer detection window. Soma may be detectable in hair samples for up to 90 days or more after the last use. This method is less common but is used in specific circumstances, such as employment drug screenings.
Symptoms Of Soma Withdrawal
Withdrawal from Soma pills can occur when the medication is reduced or discontinued after prolonged use.
Common symptoms of Soma withdrawal include:
Anxiety
Many individuals may experience heightened anxiety levels or panic attacks as their bodies adjust to the absence of the medication.
Insomnia
Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can be a common withdrawal symptom, leading to fatigue and decreased overall well-being.
Muscle Pain and Spasms
As Soma is a muscle relaxant, withdrawal can result in the return of muscle pain and spasms that the medication was initially prescribed to alleviate.
Tremors
Some individuals may experience shaking or tremors in their hands or limbs as their body reacts to the absence of the drug.
Nausea and Vomiting
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea can occur during withdrawal.
Headaches
Withdrawal can lead to increased frequency and severity of headaches in some individuals.
Increased Heart Rate
Some people may notice a faster heart rate or palpitations as a physical response to withdrawal.
Mood Changes
Withdrawal can result in mood swings, irritability, or feelings of depression, impacting an individual’s emotional well-being.
Cravings
Individuals may experience strong cravings for Soma or other substances as they navigate withdrawal.
Safe Usage And Recommendations
Using the Soma pill safely requires adherence to prescribed guidelines and an understanding of its potential risks. Here are key recommendations for safe and effective use.
-
Follow the prescribed dosage.
-
Soma is typically intended for short-term use, usually up to two to three weeks.
-
Combining soma with alcohol, benzodiazepines, or other CNS depressants can amplify sedation and increase the risk of severe side effects.
-
Inform your healthcare provider about other medications
-
Soma can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. Avoid driving, operating heavy machinery, or engaging in activities that require full alertness while using this medication.
-
If you need to stop taking soma, consult your healthcare provider to develop a tapering plan. Abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms, especially after prolonged use.
-
If your symptoms persist beyond the recommended treatment period, consult your doctor for alternative therapies rather than continuing soma independently.
How To Flush Soma Out Of Your System?
Several activities can speed up the process of Soma excretion from the human body.
As shown in the image below, the four activities can effectively accelerate Soma pill excretion. However, we suggest you consult a physician before using these tips.
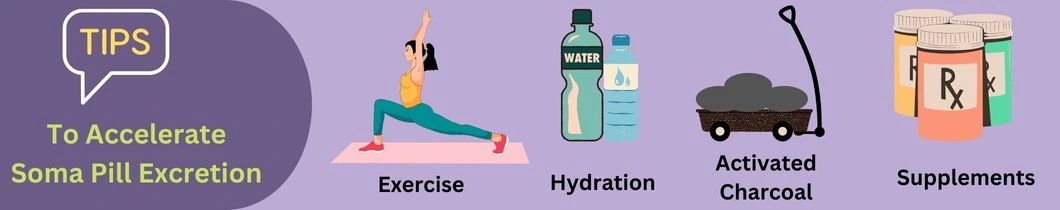
Daily Exercise-
Exercising lowers the possibility of Meprobamate accumulating in the body. Therefore, daily exercise can alter how long Soma stays in the system.
Any form of physical activity will help burn body fat and facilitate the faster elimination of Carisoprodol and Meprobamate. Running or jogging can help if you do not wish to indulge in an intense workout routine.
Using Supplements-
Health supplements like calcium-D-glucarate can help in clearing the renal detoxification pathways. It helps speed up the elimination of Soma from the body.
Activated Charcoal-
A 1986 case report by E Hassan suggests that activated charcoal can increase drug clearance from the body. It works by binding to the drug's residue in the digestive system and eliminating it. However, activated charcoal must be used only under the guidance of a physician.
Level Of Hydration-
Increased water intake can also help improve the process of removing Soma from the body by speeding up the renal system.
Our Final Thoughts On How Long Does Soma Stay In The System
Understanding how long Soma stays in your system is essential for safe and informed use. Factors such as metabolism, age, dosage, and overall health significantly influence how long the drug remains active and detectable. While Soma is generally eliminated from the body within a few days, its metabolites may linger longer and could be detected in certain drug tests.
Safe usage practices, including adhering to prescribed doses and avoiding prolonged use, can help minimize risks associated with Soma. If you are concerned about detection times, withdrawal symptoms, or the effects of Soma on your health, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial.